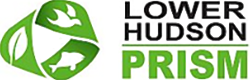- Terrestrial Plants
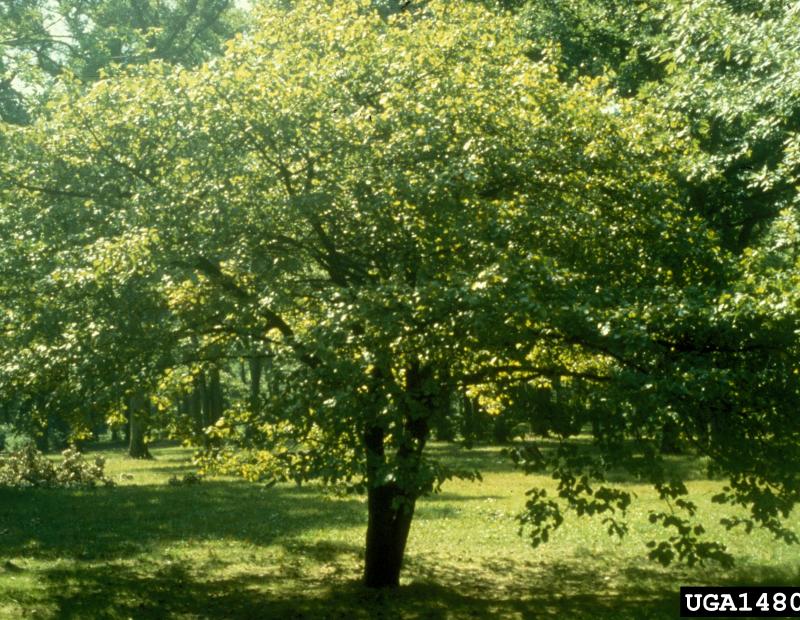
- Tree
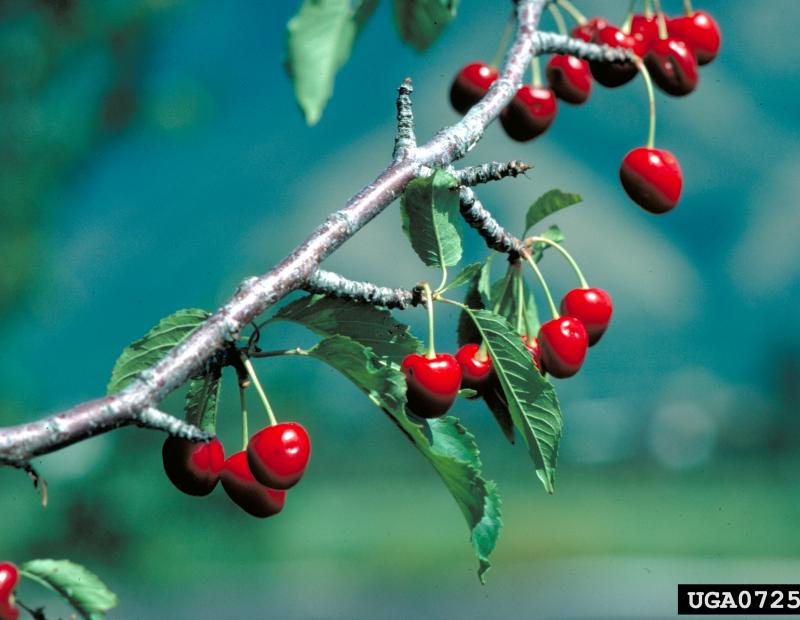
Many animals favor the fruits of this tree, they will further its' spread to new locations. It is a very fast growing tree, and reproduce quicker than other trees of similar size. Because of their life cycle, these trees can create dense stands. It can also hybridize with native cherries. These trees pose a health risk to certain animals due to glycosides that can be found in the leaves, stems and fruits.
Bird cherry, also known as sweet cherry is native to Europe, northern Africa, southwestern Asia. It is an introduced ornamental tree that grows up to 10 m. tall. It has been used as a cultivar for other cherries, and has been figured to have escaped from cultivation. By being visually appealing and producing edible berries, it was frequently planted in gardens as well.
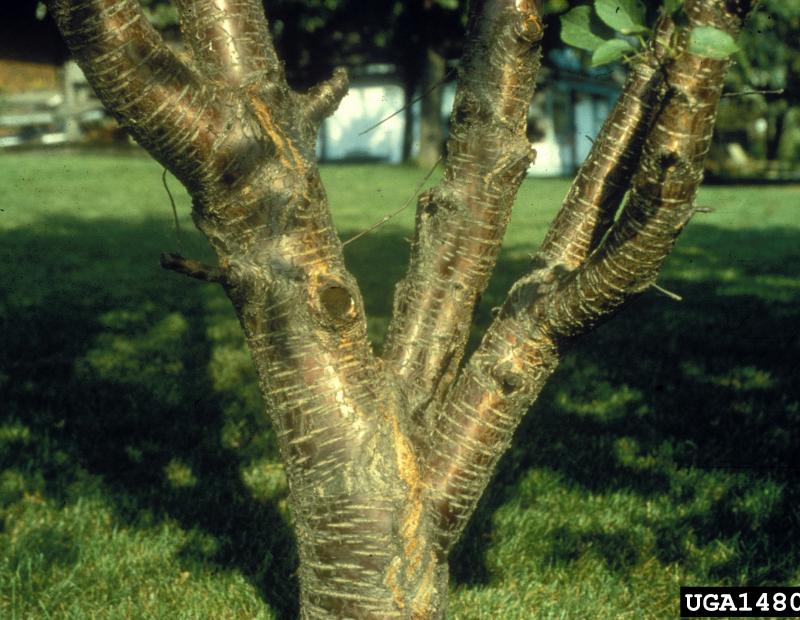
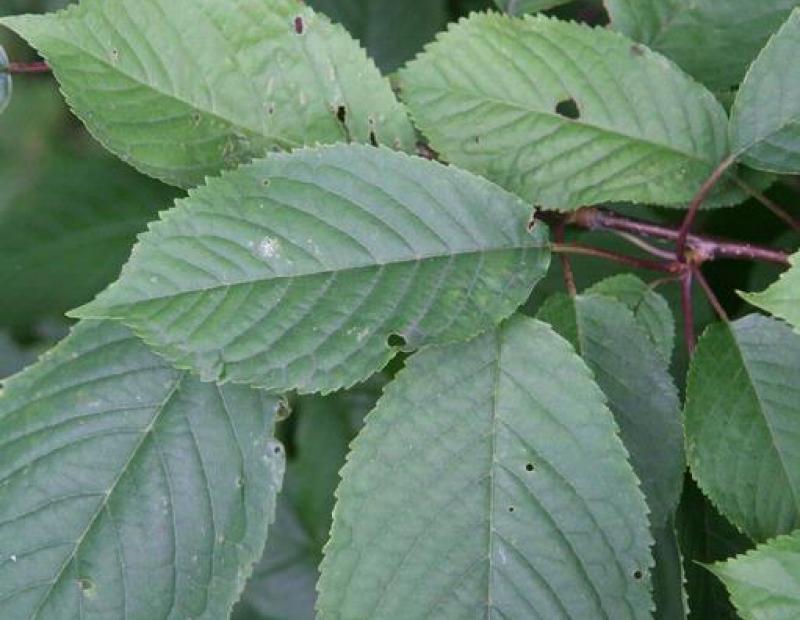
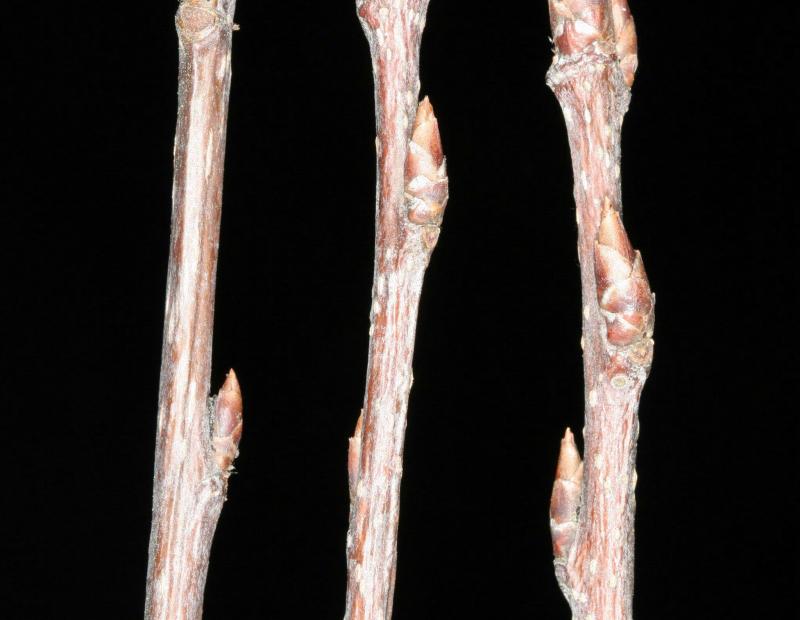
Prunus avium has alternate, simple leaves, between 2 and 5 inches long, that are oval to obovate, with a serrated margin. Pronounced darkened glands on the petiole, generally with atleast 8 or more pairs of veins. The flowers are very showy, white, 1-inch across, 3-5 per clusters, and appear early on in the spring. They have dark red to nearly blackfruits, and may be clustered on spur shoots and mature between early to mid-summer. The bark of the tree is dark gray in color, smooth, with prominant, long horizontal lenticels.
This tree grows best in average, medium moisture, well drained soils in full sun. They prefer moisture retentive-soils that have good drainage. Bird tree is widespread throughout the Lower Hudson region.